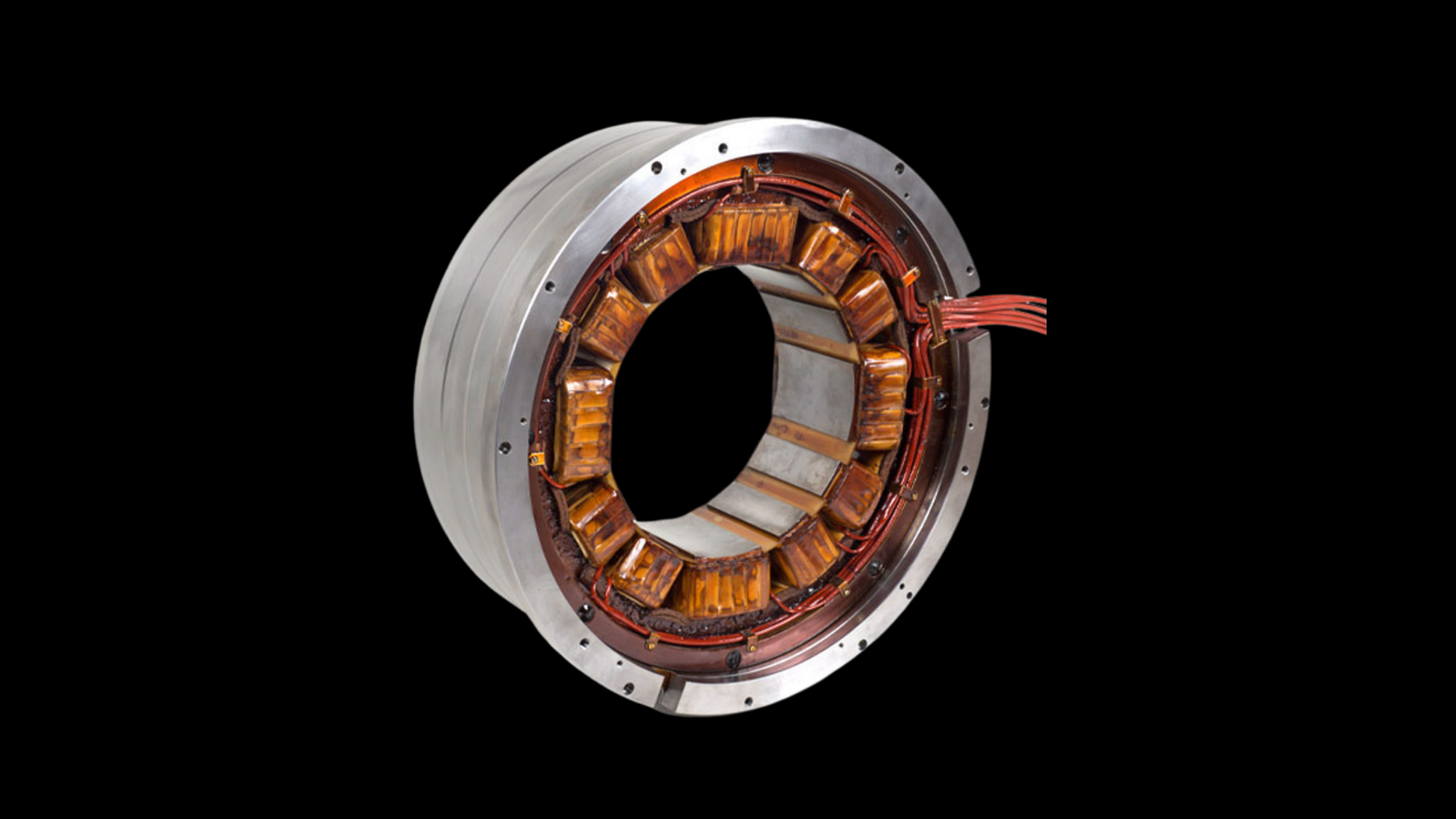
Heat pumps are at the center of industrial decarbonization, offering a clean alternative to fossil-fuel boilers. But when it comes to high-temperature heat pumps, which can deliver heat above 120 °C for demanding sectors like food and beverage, pulp & paper, chemicals and pharma, and textiles, the compressor is the heart of the system. One of the most exciting innovations in compressor design today is magnetic levitation. So why does this matter, and why is it especially valuable in high-temperature applications?
1. Frictionless Operation = Higher Efficiency
Traditional compressors use active mechanical bearings that create friction, heat, and wear. In contrast, magnetic levitation suspends the shaft in a magnetic field, allowing it to spin without contact.

- No friction means less energy lost and higher compressor efficiency.
- For high-temperature heat pumps, where large temperature lifts demand more compressor work, reducing internal losses directly improves the coefficient of performance (COP). Studies show COPs of 2.5–5.8 for industrial high-temperature heat pumps, depending on temperature lift — maglev helps push performance to the upper range.
2. Reliability Under Extreme Conditions
High-temperature heat pumps often operate at high pressures and thermal stresses. Mechanical bearings are more prone to wear, lubrication breakdown, and costly downtime.
- Maglev eliminates the need for oil lubrication altogether.
- This means stable performance at higher discharge temperatures, reduced maintenance, and extended equipment lifetime.
For industries like pulp & paper ansignificant cost savings.
3. Oil-Free Compression = Cleaner Heat
Conventional bearings require oil lubrication, which by design enters into the working cycle. In high-temperature systems, this is even more problematic:
- Oil reduces heat transfer efficiency as it clogs the heat exchanger surfaces.
- It can degrade at high discharge temperatures, limiting the maximum heat supply.
- Neither the working fluid (”refrigerant”) nor the oil like each other. They both contaminate and inhibit normal function; the working fluid doesn’t evaporate as it should, and the oil doesn’t lubricate.
Maglev compressors are completely oil-free, ensuring clean, efficient heat transfer. This is true for all industries as better efficiency means higher savings.
4. Compact, Quiet, and Scalable
Magnetic levitation allows for high-speed, lightweight compressors. These can be built in a more compact form factor than traditional heavy-duty machines.
- For retrofits into existing plants, a smaller footprint is a major advantage.
- Factory-built units can be fully tested before shipping, shortening the commissioning phase
- Lower vibration and noise also improve the working environment.
5. Enabling Higher Temperatures and Decarbonization
The key challenge in industrial decarbonization is replacing steam boilers operating at 120–200 °C and beyond.
- Maglev compressors make it technically and economically feasible to design high-temperature heat pumps, that can reliably deliver steam at these temperatures.
- This enables industries like food and beverage, chemicals and pharma, pulp, paper and wood as well as textiles – responsible for a large share of industrial emissions – to replace fossil-fuel boilers with electrified, efficient solutions.
Summary
Magnetic levitation technology transforms the performance of high-temperature heat pumps by:
- Boosting efficiency through frictionless operation
- Eliminating oil and contamination risks
- Increasing reliability at extreme conditions
- Reducing maintenance and extending service life
- Enabling higher temperature ranges required for industrial decarbonization
For industries under pressure to reduce costs and emissions, maglev-driven high-temperature heat pumps are not just a technological upgrade, they’re a pathway to future-proof, sustainable heating.